BinaryTreePruning [source code]
public class BinaryTreePruning {
static
/******************************************************************************/
class Solution {
public TreeNode pruneTree(TreeNode root) {
containsOne (root);
return root;
}
boolean containsOne (TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
// tricky base case
return false;
boolean left = containsOne (root.left), right = containsOne (root.right);
if (!left) {
root.left = null;
}
if (!right)
root.right = null;
return left || right || root.val == 1;
}
}
/******************************************************************************/
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTreePruning.Solution tester = new BinaryTreePruning.Solution();
}
}
除了leaf的base case稍微需要思考一下, 本身题目不是很难, 想到mutation recurison和returned recursion混合使用就行了;
UNFINISHED
uwi:
class Solution {
public TreeNode pruneTree(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root);
}
TreeNode dfs(TreeNode cur)
{
if(cur == null)return null;
boolean hasone = false;
if(cur.left != null){
cur.left = dfs(cur.left);
if(cur.left != null)hasone = true;
}
if(cur.right != null){
cur.right = dfs(cur.right);
if(cur.right != null)hasone = true;
}
if(hasone || cur.val == 1){
return cur;
}else{
return null;
}
}
}
没仔细看, 不过这个题目本身也不难;
cchao:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* pruneTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return root;
root->left = pruneTree(root->left);
root->right = pruneTree(root->right);
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr && root->val == 0)
return nullptr;
return root;
}
};
Problem Description
We are given the head node root of a binary tree, where additionally every node's value is either a 0 or a 1.
Return the same tree where every subtree (of the given tree) not containing a 1 has been removed.
(Recall that the subtree of a node X is X, plus every node that is a descendant of X.)
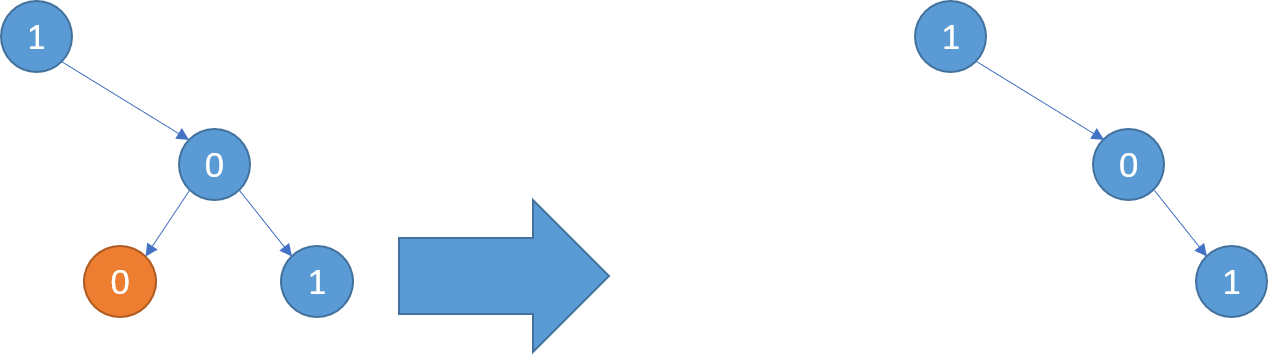
Example 1:
Input: [1,null,0,0,1]
Output: [1,null,0,null,1]
Explanation:
Only the red nodes satisfy the property "every subtree not containing a 1".
The diagram on the right represents the answer.
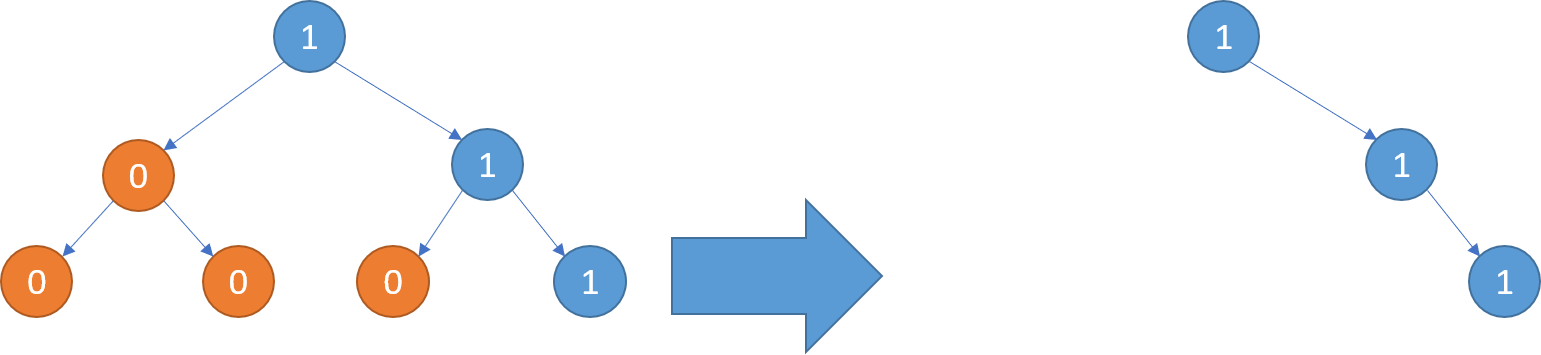
Example 2:
Input: [1,0,1,0,0,0,1]
Output: [1,null,1,null,1]
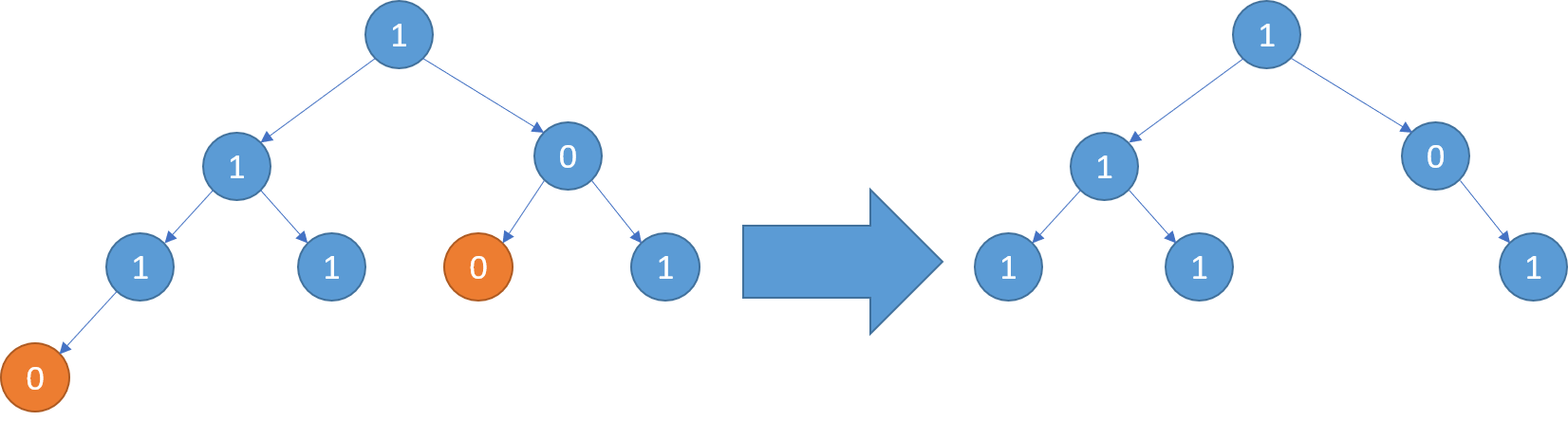
Example 3:
Input: [1,1,0,1,1,0,1,0]
Output: [1,1,0,1,1,null,1]
Note:
- The binary tree will have at most 100 nodes.
- The value of each node will only be 0 or 1.
Difficulty:Medium
Total Accepted:1.3K
Total Submissions:1.7K
Contributor:awice
Companies
hulu
Related Topics
tree